"From the Modern Synthesis to the Inclusive Evolutionary Synthesis: An Einsteinian Revolution in Evolution"
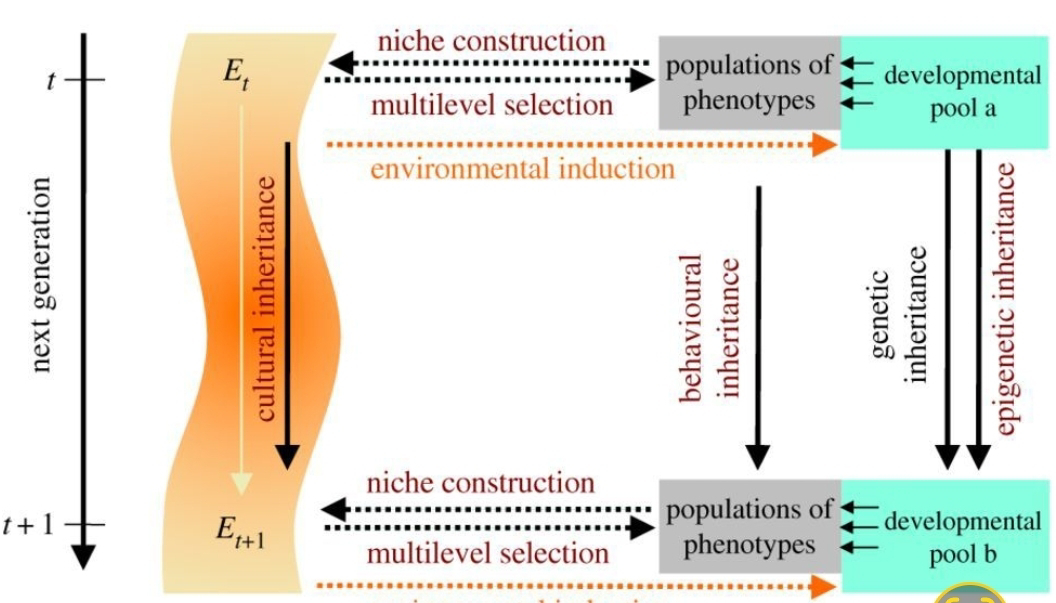
Article by Danchin. The Modern Synthesis (MS) is the prevailing theory of evolution in biology. It was developed in the early 20th century by a group of scientists who integrated Darwin's theory of natural selection with the new science of genetics. The MS holds that evolution is driven by the differential reproduction of genes that confer a fitness advantage in a particular environment. In recent years, however, there has been growing dissatisfaction with the MS. This is because the MS does not adequately account for the role of non-genetic factors in evolution, such as epigenetics, developmental plasticity, and culture. Epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence. These changes can be inherited from one generation to the next, and they can have a significant impact on the phenotype (observable characteristics) of an organism. Developmental plasticity is the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to its environment. This can be adaptive, as it allows organisms to adapt to changing environmental conditions. Culture is the transmission of knowledge, beliefs, and practices from one generation to the next. It is a powerful force of evolution, as it can allow organisms to acquire new traits that are not encoded in their genes. The Inclusive Evolutionary Synthesis (IES) (aka EES) is a new paradigm in evolutionary biology that seeks to go beyond the MS with these non-genetic factors. The IES holds that evolution is a multi-level process that involves the interaction of genes, epigenetics, development, and culture. The IES is still under development, but it has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of evolution. It could help us to better understand the evolution of complex traits, such as intelligence and behavior. It could also help us to develop new strategies for conservation and management of natural populations. The IES is an Einsteinian revolution in evolution. Just as Einstein's theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of physics, the IES is revolutionizing our understanding of evolution. It is a new paradigm that is challenging our old assumptions about how evolution works. The IES is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to have a profound impact on our understanding of life. It could help us to better understand the origins of life, the evolution of complex traits, and the future of humanity. Here are some of the key features of the IES:
It is a multi-level theory that takes into account the interaction of genes, epigenetics, development, and culture.
It emphasizes the importance of non-genetic inheritance in evolution.
It recognizes that evolution is a complex and dynamic process that is influenced by many factors.
It is open to new ideas and evidence.
The IES is a promising new paradigm that has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of evolution. It is still in its early stages, but it is already generating a lot of excitement and debate among evolutionary biologists. Only time will tell how the IES will ultimately shape our understanding of life, but it is clear that it is a major step forward in our understanding of evolution. In addition to the key features mentioned above, the IES also has a number of implications for our understanding of evolution. For example, the IES suggests that evolution is not always gradual and predictable. It can also be rapid and discontinuous, and it can be influenced by chance events. The IES also suggests that evolution is not always driven by natural selection. Other forces, such as genetic drift and cultural evolution, can also play a role. The IES is a complex and challenging theory, but it is also a powerful one. It has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of evolution and to help us to better understand the natural world.


Comments
Post a Comment