Rethinking Human Origins: A Paradigm Shift in Evolutionary Theory
The special issue of PaleoAnthropology, titled "Niche Construction, Plasticity, and Inclusive Inheritance: Rethinking Human Origins with the Extended Evolutionary Synthesis (EES)", presents a compelling case for re-evaluating the traditional understanding of human evolution. This collection of articles challenges the prevailing Modern Synthesis theory, arguing that a broader framework is necessary to fully grasp the complexities of human origins.
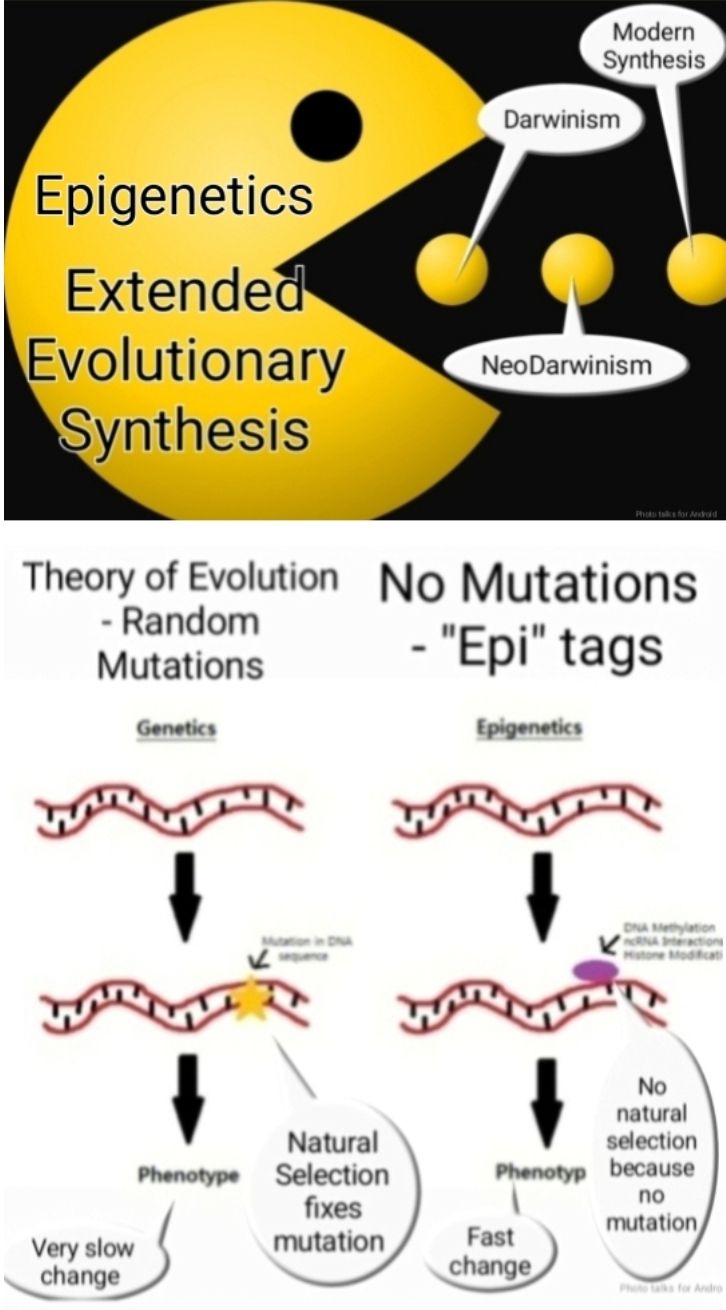
Beyond the Modern Synthesis
The Modern Synthesis, which has dominated evolutionary biology for decades, emphasizes the role of genetic variation and natural selection in driving evolutionary change. While this model has provided insights, the EES proposes that it is incomplete. The EES argues that additional factors, such as niche construction, developmental plasticity, and inclusive inheritance, have played a significant role in shaping the human lineage.
Niche construction refers to the ability of organisms to modify their environment, which can subsequently influence their own evolution and that of other species. Developmental plasticity is the capacity of organisms to alter their development in response to environmental cues, leading to different phenotypes from the same genotype. Inclusive inheritance encompasses the transmission of traits not only through genes but also through epigenetic modifications and cultural practices.
Key Themes in the Special Issue
This article explores these concepts in depth, offering a diverse range of perspectives on their implications for understanding human origins. Several recurring themes emerge from this article.
The importance of niche construction: The article highlights the role of niche construction in human evolution, arguing that our ancestors actively shaped their environments through activities such as toolmaking, fire use, and agriculture. These modifications not only facilitated survival and reproduction but also created new selective pressures that influenced subsequent evolutionary trajectories.
The role of developmental plasticity: The authors emphasize the importance of developmental plasticity in allowing humans to adapt to diverse and changing environments. This flexibility enabled our ancestors to colonize new habitats and exploit novel resources, contributing to our species' remarkable ecological success.
The significance of inclusive inheritance: The article discuss the transmission of cultural knowledge and practices as a form of inheritance that has shaped human evolution. This cultural evolution has interacted with genetic and epigenetic processes, creating a complex and dynamic interplay that has driven the emergence of unique human traits such as language, technology, and social organization.
Implications for Paleoanthropology
The EES offers a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of human evolution than the Modern Synthesis. By incorporating niche construction, developmental plasticity, and inclusive inheritance, the EES provides a framework for integrating diverse lines of evidence from genetics, paleontology, archaeology, and anthropology. This integrated approach has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of human origins and shed new light on the processes that have shaped our species.
Criticisms and Future Directions
While the EES has gained significant traction in recent years, it has also faced criticism from some evolutionary biologists who argue that it does not represent a fundamental departure from the Modern Synthesis. They contend that the concepts of niche construction, developmental plasticity, and inclusive inheritance can be accommodated within the existing framework.
However, proponents of the EES maintain that it offers a more comprehensive and integrated perspective that is better suited to addressing the complexities of human evolution. They argue that the EES has the potential to stimulate new research questions and foster interdisciplinary collaboration, ultimately leading to a deeper understanding of our origins.
Conclusion
The special issue of PaleoAnthropology represents a significant contribution to the ongoing debate about the nature of human evolution. By highlighting the importance of niche construction, developmental plasticity, and inclusive inheritance, the EES challenges us to rethink our understanding of the processes that have shaped our species. While the EES is still a developing framework, it offers a promising avenue for future research and has the potential to transform our understanding of human origins.


Comments
Post a Comment